Secondary Academic Programs
Secondary Academic Program Competencies
Secondary Academic Programs Summary
Secondary Academic Programs is simply another way of saying, students with disabilities should be included within general education classrooms. Research shows that student's in a predominately isolated classroom have a lesser chance of obtaining the following goal-oriented ideologies: postsecondary educational success, employable job skills, and viable independent living skills (Clavenna-Deane and Morningstar, 2018). Students with disabilities should have access to the general education curriculum in order to not only gain skills related to transition but to function in an environment with students without disabilities. A great way for transition coordinators to facilitate transition-focused skills and classes for students with disabilities and without disabilities, is by using a Universal Design approach for Learning (UDL), utilizing the Oneder curriculum, and applying accommodations and modifications (including assistive technology). The following artifacts demonstrate mastery of each competency through each of the following approaches.
Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
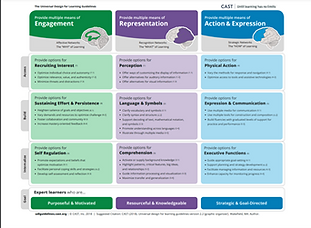
UDL is designed to expand learning to all students. As stated by Burgstahler (2012),"The goal of UDI is to maximise the learning of students with a wide range of characteristics by applying UD principles to all aspects of instruction (e.g., delivery methods, physical spaces, information resources, technology, personal interactions, assessments)." It focuses on meeting the instructional needs of all students in the areas of technology, assessments, curriculum, classroom environment, and teacher's delivery methods. Instead of adapting or modifying an individual student's learning, UDL focuses on the instruction of the class as a whole through the multiple means of representation, multiple means for action and expression, and the multiple means of engagement. The following artifact examines the UDL guidelines and also provides a sample lesson plan that incorporates the three areas of UDL: Action and Expression, Representation, and Engagement. (4.1, 4.2, 4.6, 4.7)
Click to enlarge artifacts
Accessing Postsecondary Education and Training
Within course 861, the final project required us to research a local college's disability services. The primary goal of this assignment was to gain familiarity with the disability services offered by a local college with hopes that this information is shared with family, students in transition, and other teachers. Georgia Institute of Technology is located within the metro-Atlanta area and is within 15 minutes of the school district. They offer various programs for students with disabilities and also provide their eligibility criteria. The following artifacts demonstrate the disability services offered at Georgia Tech. (4.3, 4.4, 4.5)
Click to enlarge artifacts
Resources
-
Burgstahler, S. (2012). Equal access: Universal Design of Instruction (UDI): definition, principles, guidelines, and examples. (Links to an external site.)University of Washington.
-
CAST (2018). Universal design for learning guidelines version 2.2 [graphic organizer]. Wakefield, MA: Author.
-
Georgia Tech ILSI. (2015 September 17). Excel at Georgia Tech. Retrieved From https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D-_mn5Mo1a8
-
Holmes, R. (2020 August 6). Access to Postsecondary Education and Training. Blending Acaedmics and Transition. University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS.
-
Holmes, R. (2020 July 6). Review of Model Lesson. Blending Acaedmics and Transition. University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS.
-
Morningstar, M. & Clavenna-Deane, B. (2018). Your Complete Guide To Transition Planning and Services. Baltimore, MD: Brookes Publishing Company.